What Is the Procedure for CE Marking?
Summary:
The CE mark is a mandatory requirement for many products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). It signifies that the product complies with essential safety, health, environmental, and consumer protection requirements set out by the European Union (EU).
Obtaining the EU CE marking demonstrates a manufacturer’s commitment to product safety and paves the way for smooth market access across the EEA.3 However, navigating the CE marking process can be complex. In this article, we have detailed the process of compliances to obtain the CE mark.

Understanding CE Marking
CE stands for Conformité Européenne, which translates from French to “European Conformity“. It’s a marking that signifies a product’s compliance with various safety, health, and environmental protection standards set by the European Union (EU).
Simply put, seeing the EU CE marking on a product means it has been assessed and deemed safe for sale and use within the European Economic Area (EEA), which includes the EU member states, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.
Significance of CE Marking
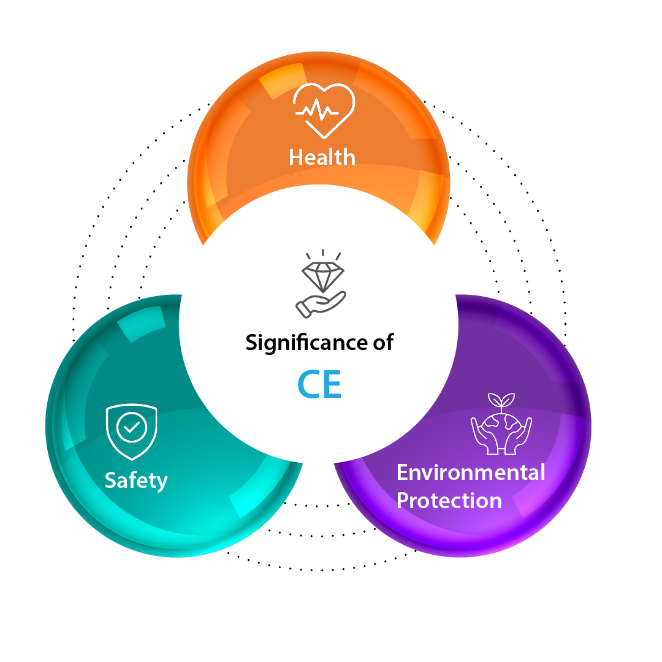
Here’s a breakdown the significance of CE Marking:
- Safety: Products with the CE marking are deemed safe for consumers, meaning they meet strict safety requirements set by the EU and pose minimal risk of injury or harm.
- Health: The CE marking also ensures the product doesn’t pose any health hazards to users. This includes regulations concerning harmful substances, noise levels, and other potential health risks.
- Environmental Protection: The CE marking indicates the product meets environmental protection standards set by the EU. This considers factors like resource efficiency, waste generation, and potential environmental impact.
By requiring the CE marking, the EU aims to:
- Ensure consumer protection: The marking helps consumers identify products that meet essential safety, health, and environmental standards.
- Facilitate fair competition: It ensures all businesses, regardless of their origin, comply with the same regulations when selling products in the EEA.
- Simplify the free movement of goods: By having a single set of standards, the CE marking allows for the smooth movement of products within the EEA without facing additional technical barriers in each member state.
Overview of the CE Marking Procedure
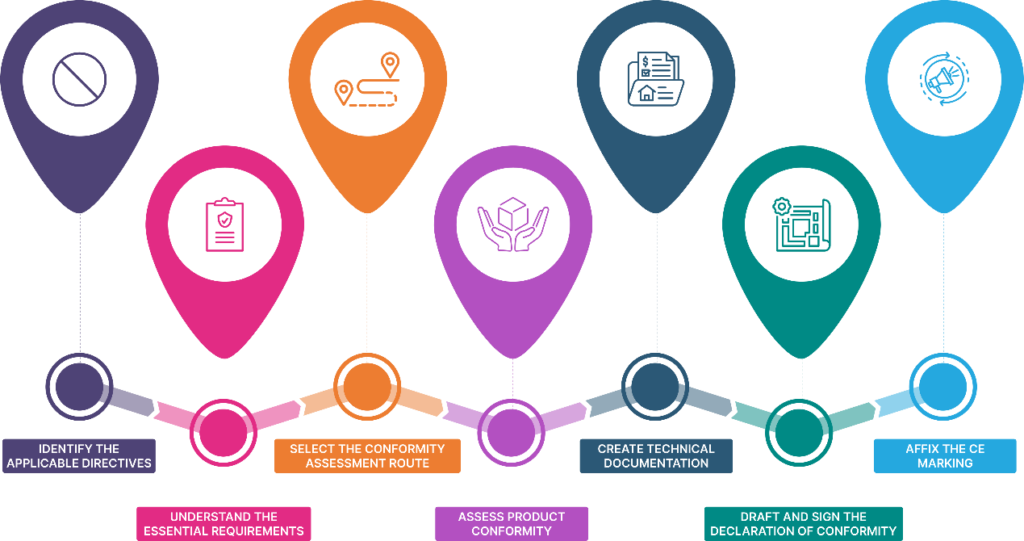
Procedure for CE Marking
Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved in the CE marking procedure:
1. Identifying the Applicable Directive
The first and extremely crucial step is identifying the relevant EU Directive(s) that your product falls under. Each Directive outlines specific essential requirements for different product categories, such as machinery, medical devices, and more. Resources like the NANDO (New Approach Notified and Designated Organisations) database and official EU websites can help you determine the relevant Directive.
2. Understanding Essential Requirements
Once you’ve identified the applicable Directive, note the specific requirements listed. These requirements address various aspects of product safety, health, and environmental protection. Carefully analyse your product against these requirements to meet the necessary standards.
3. Determining Conformity Assessment Route
The CE Marking process involves self-declaration of conformity by the manufacturer. However, depending on the product category and associated risks, the involvement of a Notified Body (an independent conformity assessment body) might be mandatory. The specific Directive will outline the applicable conformity assessment modules and whether an independent assessment is required.
4. Assessing Product Conformity
This stage involves conducting various assessments to ensure your product meets the essential requirements. This may include one or more of the eight modules defined by the regulatory authorities – internal production control measures, risk assessments, testing by notified bodies or accredited laboratories, and technical inspections, etc. Documenting these assessments meticulously is crucial for the next step.
5. Preparing Technical Documentation
Compile a comprehensive technical documentation file that serves as evidence of your product’s compliance with the essential requirements. This file typically includes product descriptions, design and manufacturing specifications, risk assessments, test reports, and technical drawings.
6. Drafting and Signing the Declaration of Conformity
The EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) is a formal document where you declare your product’s compliance with the relevant legislation and take full responsibility for its safety. It must be signed by a person authorized to represent your company and kept readily available for authorities.
7. Affixing the CE Marking
Once you’ve completed the previous steps and are confident in your product’s compliance, you can affix the CE Marking to your product. The mark must be visible, legible, and indelible. Remember, affixing the CE Marking signifies full responsibility for compliance and represents a commitment to ongoing product safety throughout its lifecycle.
Is There A Fee?
If you conduct the conformity assessment yourself, you won’t have to pay any fees. You must, however, pay the notified body if the EU specifications applicable to your product require an independent assessment. It depends on the certification procedure, the complexity of the product and how much it will cost.
Additional Considerations For CE Marking Procedure
- Seeking guidance from notified bodies or specialized consultants can be beneficial, especially for complex products or if you’re unfamiliar with the CE marking procedure.
- Staying updated on regulatory changes is crucial, as Directives and standards are periodically revised.
Conclusion
Understanding the CE marking procedure empowers manufacturers to navigate the requirements and ensure their products meet the necessary safety and regulatory standards for successful market access within the EEA. Remember, this article provides a general overview, and you should always refer to the specific Directive(s) and consult relevant resources for comprehensive and up-to-date information.
References
- van Economische Zaken en Klimaat M. What products must have CE marking? [Internet]. Government.nl. 2016 [cited 2024 Feb 28]. Available from: https://www.government.nl/documents/questions-and-answers/what-products-must-have-ce-marking
- Press corner [Internet]. European Commission – European Commission. 2010 [cited 2024 Feb 28]. Available from: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/de/MEMO_10_257
- Canada GA. Six Steps to CE Marking [Internet]. GAC. 2019 [cited 2024 Feb 28]. Available from: https://www.tradecommissioner.gc.ca/guides/133383.aspx?lang=eng
- CE marking [Internet]. Your Europe. 2024 [cited 2024 Feb 28]. Available from: https://europa.eu/youreurope/business/product-requirements/labels-markings/ce-marking/index_en.htm
- CE marking [Internet]. Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs. [cited 2024 Feb 28]. Available from: https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/single-market/ce-marking_en
- European standards [Internet]. Europa. eu. [cited 2024 Feb 28]. Available from: https://osha.europa.eu/en/european-standards
- L_2014096EN.01000101.xml [Internet]. Europa. eu. [cited 2024 Feb 26]. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX%3A32014L0028
- Technical documentation and EU declaration of conformity [Internet]. Your Europe. 2022 [cited 2024 Feb 26]. Available from: https://europa.eu/youreurope/business/product-requirements/compliance/technical-documentation-conformity/index_en.htm
- CE marking [Internet]. Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs. [cited 2024 Feb 26]. Available from: https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/single-market/ce-marking_en
CliniExperts - Your reliable partner for Comprehensive Compliance Solutions. We offer 360 degree regulatory solutions to Medical Devices and In-Vitro Diagnostics.
CliniExperts
CliniExperts Services Pvt. Ltd.
Contact us
Please feel free to talk to us if you have any questions. We endeavour to answer within 24 hours.




