Understanding Medical Device Registration in Europe – A Comprehensive Guide to EU MDR
Summary:
Navigating the regulatory landscape for medical devices in the European Union (EU) can be intimidating, particularly when it comes to registration. This in-depth guide aims to empower manufacturers with the knowledge needed to navigate the medical device registration EU process effectively, ensuring their medical devices reach the European market with MDR compliance and confidence.

The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The (MDR) Medical Device Registration in Europe (Regulation (EU) 2017/745) came into full effect in May 2021, replacing the previous Medical Devices Directive (MDD). The MDR introduces stricter requirements than the MDD, aiming to enhance the safety, quality, and transparency of medical devices available in the EU.
Key Aspects of Medical Device Registration
- Classification:
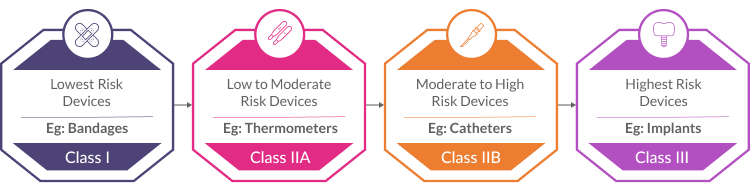
The first step is to classify your device according to its intended purpose and inherent risks. The MDR establishes four risk classes:
- Class I (Lowest Risk): Simple devices like bandages or tongue depressors.
- Class IIa (Low to Moderate Risk): Devices like thermometers or surgical drapes.
- Class IIb (Moderate to High Risk): Devices like catheters or infusion pumps.
- Class III (Highest Risk): High-risk devices like implants or life-sustaining equipment.
The classification determines the conformity assessment route needed for CE marking, which is the mandatory mark for placing medical devices on the EU market.
- Unique Device Identification (UDI):
All medical devices in the EU must have a Unique Device Identification (UDI) system. This unique identifier allows for efficient traceability, vigilance, and market surveillance. Manufacturers need to assign UDIs to their devices and submit them to the European Database on Medical Devices (EUDAMED).
- EUDAMED Registration:
EUDAMED is a central database that stores information on all medical devices and benefactors involved in the supply chain within the EU. Manufacturers are mandated to register themselves and their devices within EUDAMED, providing comprehensive details such as:
- Device information: Product name, intended purpose, technical specifications, etc.
- Technical documentation: Demonstrating device safety, performance, and quality.
- Person Responsible for Regulatory Compliance (PRRC) contact details: An EU-based individual responsible for ensuring MDR compliance throughout the device’s lifecycle.

- Conformity Assessment Procedures:
The specific conformity assessment procedure applicable to your device hinges on its risk class. Lower-risk devices (Class I and IIa) generally involve fewer complex procedures, while higher-risk devices (Class IIb and III) necessitate the involvement of a Notified Body. These independent organisations, designated by the EU, assess compliance with the MDR’s requirements. Depending on the class, conformity assessment procedures may involve:
- Internal production control system audits.
- Technical documentation review by a notified body.
- Clinical investigation and evaluation by a notified body.
Additional Considerations
To guarantee their safety and proper operation, medical devices have to pass a conformance evaluation conducted by the European Union (EU). The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is involved in the regulation process, however medical devices are also regulated at the level of EU Member States.
- Technical Documentation: Manufacturers must compile comprehensive technical documentation demonstrating their device’s safety, performance, and quality in accordance with MDR requirements. This documentation forms the basis for conformity assessment by notified bodies.
- Person Responsible for Regulatory Compliance (PRRC): Appointing a PRRC established within the EU is mandatory. This individual assumes responsibility for ensuring MDR compliance throughout the device’s lifecycle, including post-market surveillance activities.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Manufacturers have ongoing obligations to monitor their devices after launch in market. This includes tasks like:
- Reporting serious adverse events and incidents to relevant authorities.
- Implementing Corrective And Preventive Actions (CAPA) to address identified risks or non-conformities.
Seeking Expert Guidance
Due to the complexities involved, it’s highly recommended for manufacturers to seek guidance from qualified regulatory consultants or legal professionals specialising in EU medical device regulations. They can help navigate the registration process, ensure compliance with the MDR requirements, and smooth the path to successful market entry in the EU.
Conclusion
Understanding and following the medical device registration EU is crucial for manufacturers aiming to bring their products to the European market. By adhering to the MDR’s requirements and seeking expert guidance when needed, manufacturers can ensure patient safety, product compliance, and a successful market presence within the EU.
Overview of the Medical Device Registration Process
| Stage | Description |
| Classification | Categorize device based on risk (Class I-III) |
| Unique Device Identification (UDI) | Assign unique identifier for traceability |
| EUDAMED Registration | Register device and details in EUDAMED database |
| Conformity Assessment | Follow procedures based on class (internal audit, notified body review, etc.) |
| Additional Considerations | Technical documentation, Person Responsible for Regulatory Compliance (PRRC), Post-Market Surveillance (reporting incidents, CAPA) |
References
- French-Mowat E. How are medical devices regulated in the European Union? J R Soc Med [Internet]. 2012;105 Suppl 1(1_suppl):S22-8. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1258/jrsm.2012.120036
- New Regulations [Internet]. Public Health. [cited 2024 Feb 29]. Available from: https://health.ec.europa.eu/medical-devices-sector/new-regulations_en
- Classification of Medical Devices and IVDs [Internet]. Eupati. eu. [cited 2024 Feb 29]. Available from: https://learning.eupati.eu/mod/page/view.php?id=935
- UDI/Devices registration [Internet]. Public Health. [cited 2024 Feb 29]. Available from: https://health.ec.europa.eu/medical-devices-eudamed/udidevices-registration_en
- EUDAMED database [Internet]. Europa. eu. [cited 2024 Feb 29]. Available from: https://ec.europa.eu/tools/eudamed/#/screen/home
- Conformity assessment [Internet]. Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs. [cited 2024 Mar 11]. Available from: https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/single-market/goods/building-blocks/conformity-assessment_en
- Baines R et al. Navigating medical device certification: A qualitative exploration of barriers and enablers amongst innovators, notified bodies and other stakeholders. Ther Innov Regul Sci [Internet]. 2023;57(2):238–50. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43441-022-00463-4
- Canada GA. Six Steps to CE Marking [Internet]. GAC. 2019 [cited 2024 Mar 15]. Available from: https://www.tradecommissioner.gc.ca/guides/133383.aspx?lang=eng
- Medical devices [Internet]. Europa. eu. [cited 2024 Feb 29]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/medical-devices
CliniExperts - Your reliable partner for Comprehensive Compliance Solutions. We offer 360 degree regulatory solutions to Medical Devices and In-Vitro Diagnostics.
International CliniExperts
CliniExperts Services Pvt. Ltd.
Contact us
Please feel free to talk to us if you have any questions. We endeavour to answer within 24 hours.




